Using Hr Diagroam Describe the Birth of a Star
Explain using complete sentences where on the HR diagram you would expect to find a giant star based on its physical properties. Use the HR diagram to describe the birth middle-age and death of a star like our Sun.

The Evolutionary Cycle Of Stars
The larger its mass the shorter its life cycle.
. After spending the majority of its life in this stage the stars core begins to gradually heat up the star. Your answer should list the 3 types of stars the Sun will be from birth to end with an explanation of why the star changes with time. Hertzsprung had plotted the luminosity of a star against its color and effective temperature.
Also take care if using magnitude to work upwards to negative values. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is named after two astronomers Danish astronomer Eijer Hertzsprung and American astronomer Henry Russell. H-R Diagram for Stars.
HertzsprungRussell diagram a plot of luminosity against surface temperature or spectral type for a group of stars. Describe the Evolution of a Sun-like Star from its birth to death using the Hertzsprung Russell Diagram. A stars mass is determined by the amount of matter that is available in its nebula the giant cloud of gas and dust from which it was bornOver time the hydrogen gas in the nebula is pulled together by gravity and it begins to spin.
This was done in 1911. A sequence of stars on the HertzsprungRussell diagram containing the majority of stars that runs diagonally from the upper left to the lower right. Astronomers use computer models to create a theoretical HR Diagram for a population.
Astronomy Lecture Number 17. Masses of stars on the HR Diagram Star clusters are groups of stars which astronomers believe were born together at roughly the same time from the same cloud of interstellar gas. Recall from The Stars.
As a star converts hydrogen to helium in its core it gradually increases in luminosity and size. Bk LD2 k stands for a constant-plug something in. As we said last time the spectral sequence O B A F G K M is a temperature sequence with the hottest stars being of type O surface temperatures 30000-40000 K and the coolest.
One of the best ways to summarize all of these details about how a star or protostar changes with time is to use a Hertzsprung-Russell HR diagram. When nuclear fusion begins a star is plotted on the left edge of the main sequence band the zero-age main sequence and then makes a slow progression up and to the right edge of the main sequence band. Stars are born in vast clouds of gas and dust.
In a future lesson on stellar evolution they will look at how stars evolve and move around the H-R diagram as they. This image tracks the life of a Sun-like star from its birth on the left side of the frame to its evolution into a red giant star on the right. Astronomers use the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram to trace the evolutionary stage of a star.
Of great importance to theories of stellar evolution it evolved from charts begun in 1911 by the Danish astronomer Ejnar Hertzsprung and independently by the US. It later becomes a star like our Sun. By definition a star of magnitude 1 is 100 brighter than one of magnitude 6.
As a star goes through the stages of its life its luminosity and temperature. Our Sun has an absolute magnitude of 48. The stars in a cluster.
On the left the star is seen as a protostar embedded within a dusty disc of material as it forms. Next measure B brightness. For more distant stars type of star gives you L.
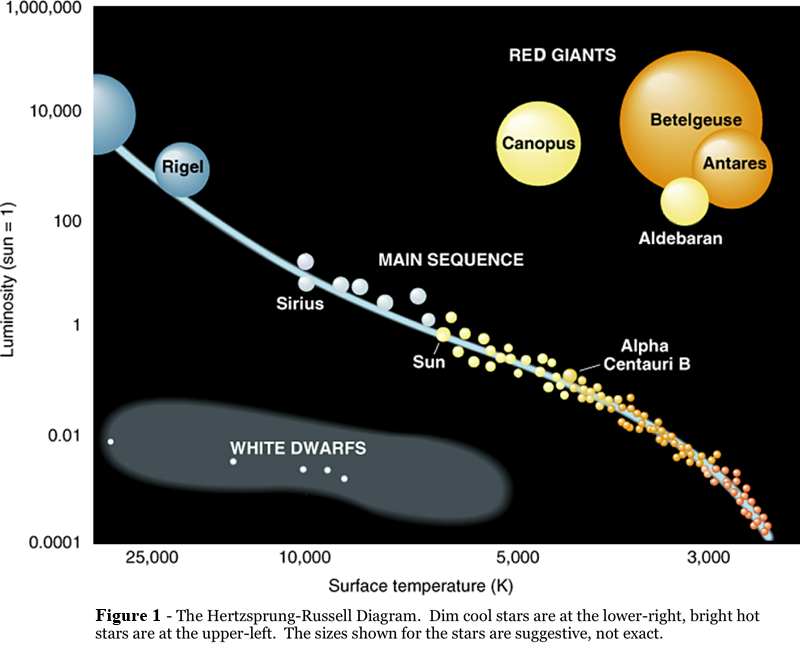
The H-R diagram is one of the fundamental tools astronomers use to classify stars. Stars eventually swell up to form a red giant star. 60 M Sun 1000 B Sun 20 M Sun Los sun sun sun VALST S 10 M Sun 100 R Sun Luminosity solar units.
Note that this is a very short distance. Describe the mass and the surface temperature of the giant stars. Describe the Evolution of a Sun-like Star from its birth to death using the Hertzsprung Russell.
Hertzsprung-Russell diagram also called H-R diagram in astronomy graph in which the absolute magnitudes intrinsic brightness of stars are plotted against their spectral types temperatures. A Celestial Census that when looking at an HR diagram the temperature the horizontal axis is plotted increasing toward the left. As the gas spins.
The Hertzsprung diagram where the evolution of sun-like stars is traced. Now calculate the stars radii in units of meters and solar radii see EQs 2 and 3. By using Parallax and trig on nearby stars to get distance valid for only few hundred LY 2.
Calculating the Radii of the Stars Using the HR Diagram in Figure 1 estimate the luminosity and temperature of all the stars listed in Table 1 and record their values in Table 1. In which stage does the Sun spend the largest amount of time and by approximately what fraction. Astronomers frequently use this technique of Main Sequence Turn-Off fitting to estimate the age of star clusters.
Describe how astronomers measure the distance to a nearby star. Life Cycles of Stars A stars life cycle is determined by its mass. This diagram is a result of the work carried out by both these astronomers independently.
HR diagrams are particularly useful for studying the characteristics of such clusters. You can draw on the diagram itself making sure to name and label each stage. Stars like the Sun end their lives as planetary nebulae and white dwarfs.
In this lesson students will look at the H-R diagram as a snapshot of all stars at a particular point in time. Classifying stars according to their spectrum is a very powerful way to begin to understand how they work. You can clearly see several different types of stars on an H-R diagram.
The way this is done in practice is the following. Calculate L luminosity 3. Stars spend most of their lives on the main sequence fusing hydrogen gas to helium gas.
You must show your calculation explicitly for at least one. This is a plot of temperature versus brightness and as stars are born live and die they move in regular patterns around the Hertzsprung-Rusell diagram. Note how the temperature scale is reversed on the horizontal axis.
Possible axes for a Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram.

H R Diagram Definition Purpose Study Com
Introduction To The Hr Diagram The Hr Diagram Named After Astronomers Hertzsprung And Russel Is A Plot Of The Surface Temperature Of A Star Versus Its Total Energy Output Which Astronomers Call Luminosity This Diagram Is Therefore An External
0 Response to "Using Hr Diagroam Describe the Birth of a Star"
Post a Comment